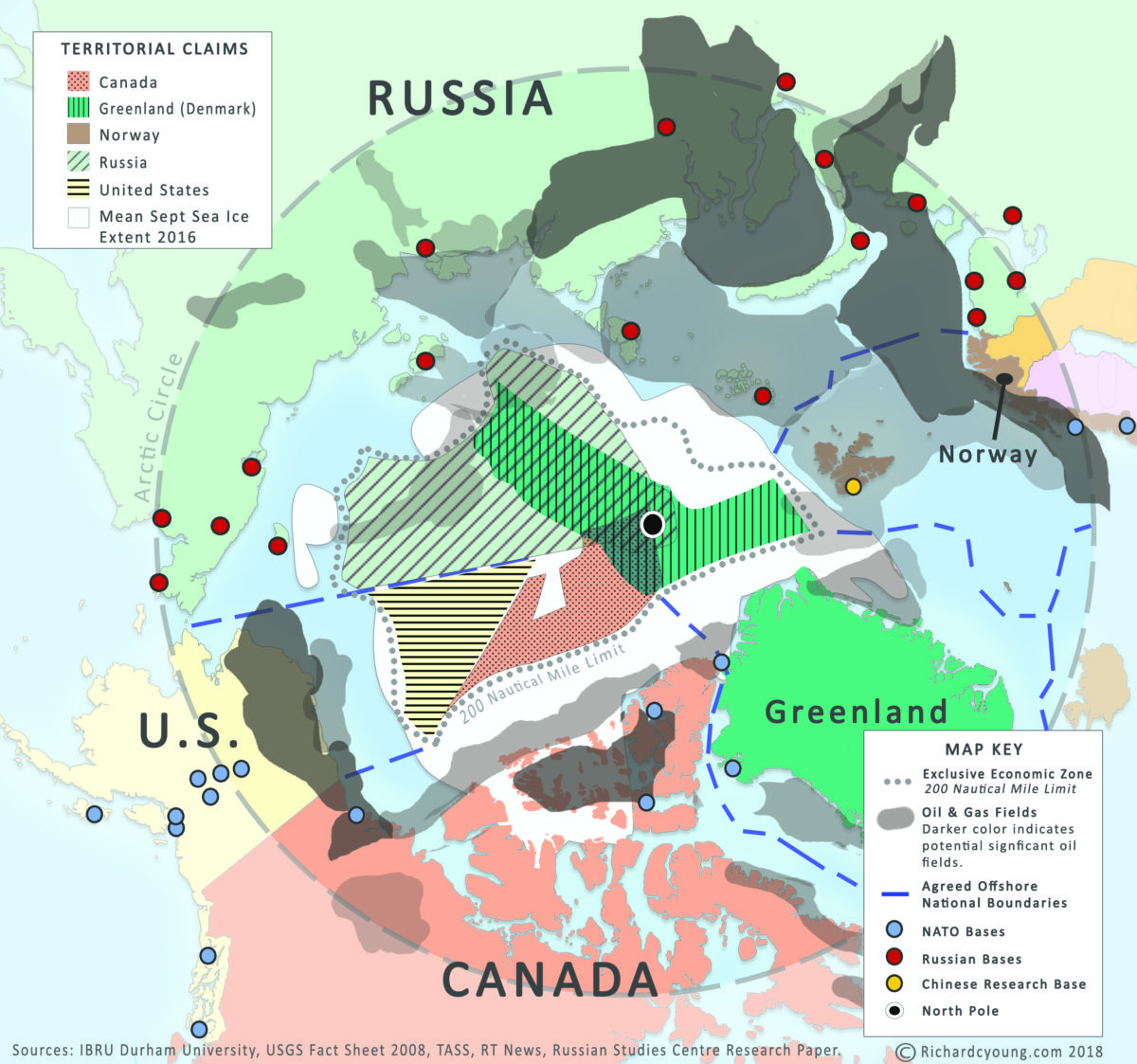
The Arctic Cold War signifies more than a mere term; it marks a profound shift in global geopolitics as nations scramble to establish their foothold in one of Earth's final frontiers. The melting ice caps have unveiled untapped resources and opened new shipping routes, transforming the Arctic into a strategic battleground. With countries like Russia, the United States, and China bolstering their military presence, the risk of conflict looms larger than ever. This underscores the necessity for a deeper understanding of the intricate dynamics unfolding in this icy expanse.
This article delves into the complexities of the Arctic Cold War, exploring the motivations driving the actions of various nations and the broader implications for global security. The Arctic is far from being a remote and barren region; it is a treasure trove of resources, including vast reserves of oil, gas, and minerals, along with emerging maritime routes that could revolutionize international trade. As climate change accelerates the melting of Arctic ice, the stakes have never been higher, making the region a focal point for geopolitical competition.
As we navigate through this article, we will examine the historical backdrop of Arctic geopolitics, the current surge in military activities, and the pressing environmental challenges accompanying these developments. By unraveling the factors fueling the Arctic Cold War, we can better comprehend its potential ramifications for the world at large.
Read also:Is June Carter Still Alive Exploring The Legacy Of A Country Music Legend
Table of Contents
- Historical Context of Arctic Geopolitics
- Current State of the Arctic Cold War
- Military Presence in the Arctic
- Resource Exploration and Exploitation
- Environmental Concerns
- International Law and Treaties
- Future Prospects and Predictions
- Conclusion
Exploring the Historical Context of Arctic Geopolitics
For centuries, the Arctic has captivated the interest of nations due to its strategic location and abundant natural resources. During the Cold War, the Arctic served as a critical theater for military operations and espionage between the United States and the Soviet Union. Even after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Arctic's significance did not diminish but rather evolved into a new era of geopolitical dynamics. The region's potential has only grown more pronounced as climate change reshapes its landscape.
The Impact of Melting Ice and New Opportunities
Recent years have witnessed a dramatic acceleration in the melting of polar ice, driven by climate change. This transformation has opened up previously inaccessible areas, sparking heightened interest from numerous nations. According to a comprehensive report by the Arctic Council, the Arctic is warming at a rate nearly double the global average, leading to profound changes in its geography and economy. These changes have not only unlocked new opportunities but also intensified competition among global powers.
Historical Treaties and Agreements
The governance of the Arctic is governed by several treaties, with the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) playing a pivotal role. This landmark agreement outlines the rights of nations to access resources on the continental shelf, providing a framework for navigating the complexities of Arctic governance. Understanding these treaties is crucial for addressing the evolving challenges in the region.
The Current State of the Arctic Cold War
As of 2023, the Arctic Cold War is marked by escalating military activities and rising diplomatic tensions among Arctic nations. Russia has been particularly aggressive in expanding its military presence, conducting large-scale training exercises and establishing new bases along its Arctic coast. In response, the United States has bolstered its naval operations and air patrols in the region, signaling its determination to assert influence and safeguard its interests.
Key Players in the Arctic Cold War
- Russia: As the nation with the largest Arctic territory, Russia's military buildup is among the most significant, with an emphasis on securing its northern borders and protecting its economic assets.
- United States: The U.S. is actively enhancing its presence in the Arctic, aiming to counterbalance Russian activities and ensure its strategic interests are preserved.
- China: Despite not being an Arctic nation, China has declared itself a "near-Arctic state" and is making substantial investments in Arctic initiatives, further complicating the geopolitical landscape.
Geopolitical Implications and Challenges
The actions of these nations have far-reaching implications for international relations. The Arctic Cold War could lead to disputes over maritime boundaries and resource claims, potentially destabilizing the region. The Arctic Council, comprising Arctic states and indigenous representatives, plays a vital role in fostering dialogue and cooperation, but tensions continue to rise as nations pursue their respective agendas.
Military Activities in the Arctic
The Arctic has emerged as a hotspot for military activities, with nations expanding their naval and air capabilities to assert dominance. Russia has reactivated military bases that were abandoned after the Cold War, significantly enhancing its capacity to project power in the region. The United States, along with its NATO allies, has responded by intensifying its military presence, including deploying submarines and conducting joint exercises with partner nations.
Read also:Judith Dench A Legacy Of Excellence In Acting
Russia's Strategic Military Buildup
Russia's military strategy in the Arctic focuses on safeguarding its northern territories and securing its economic interests. The establishment of new military bases and the modernization of its naval fleet are integral components of this strategy, reflecting Russia's commitment to maintaining a strong presence in the Arctic.
U.S. and NATO's Countermeasures
The United States, in collaboration with NATO allies, has stepped up its military presence in the Arctic as a counterbalance to Russian activities. Joint military exercises, enhanced surveillance, and the deployment of advanced weaponry are key elements of this effort to ensure freedom of navigation and deter potential aggression. This coordinated response underscores the importance of collective security in the region.
Resource Exploration and Its Implications
The Arctic is home to an abundance of natural resources, including vast reserves of oil, gas, and minerals. As the ice continues to melt, the potential for exploration and exploitation grows, attracting the attention of major energy companies. However, this resource rush raises serious concerns about environmental degradation and the rights of indigenous communities who have inhabited the region for generations.
The Promise and Challenges of Oil and Gas Reserves
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, the Arctic is estimated to hold approximately 13% of the world's undiscovered oil reserves and 30% of its undiscovered natural gas. The competition to secure these resources is intensifying, with nations vying for control over lucrative extraction opportunities. This scramble for resources could lead to disputes and conflicts if not managed carefully through international cooperation.
Protecting Indigenous Communities
Resource exploration in the Arctic poses significant risks to the traditional ways of life of indigenous peoples. Their rights and voices must be respected and included in all discussions surrounding resource extraction, as they are directly impacted by these developments. Balancing economic interests with the preservation of cultural heritage is essential for sustainable development in the region.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
The Arctic represents one of the planet's most delicate ecosystems, and the rise in human activity raises critical environmental concerns. Oil spills, habitat destruction, and the effects of climate change are pressing issues that demand immediate attention. Protecting the Arctic environment is not only vital for preserving local wildlife but also for mitigating global environmental challenges.
Climate Change and Its Global Impact
The rapid pace of climate change in the Arctic has far-reaching consequences, affecting not only wildlife but also contributing to rising sea levels and altering weather patterns worldwide. The melting of polar ice caps is accelerating, leading to cascading effects that could disrupt ecosystems and economies on a global scale. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated international effort to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Regulatory Measures and International Cooperation
International cooperation is indispensable for addressing the environmental challenges facing the Arctic. Treaties and agreements aimed at protecting the Arctic environment are crucial, but ensuring their effective implementation remains a significant challenge. Strengthening regulatory frameworks and enhancing enforcement mechanisms will be essential for safeguarding this fragile region.
The Legal Framework Governing Arctic Affairs
Understanding the legal architecture governing the Arctic is vital for resolving disputes and fostering peaceful cooperation. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) serves as the primary legal instrument, establishing maritime boundaries and rights to resources. However, implementing these laws in the Arctic's complex geopolitical landscape presents unique challenges.
Key Treaties Shaping Arctic Governance
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS): This treaty establishes the legal framework for maritime boundaries and resource rights, providing a foundation for resolving disputes in the Arctic.
- Arctic Council: This intergovernmental forum facilitates cooperation among Arctic states and indigenous peoples, promoting sustainable development and environmental protection in the region.
Challenges in Enforcing International Laws
Enforcing international laws in the Arctic poses significant challenges, particularly with competing territorial claims. Diplomatic solutions are essential to prevent conflicts from escalating and ensuring that disputes are resolved peacefully. Strengthening international institutions and fostering dialogue among stakeholders will be crucial for maintaining stability in the region.
Future Prospects and Predictions
The future trajectory of the Arctic Cold War remains uncertain, shaped by the ongoing climate crisis, geopolitical rivalries, and the competition for resources. The interplay of these factors will determine the future of international relations in the Arctic region, with potential scenarios ranging from increased cooperation to escalating tensions.
Possible Scenarios in the Arctic's Future
- Enhanced Cooperation: Nations may recognize the importance of collaboration in addressing shared challenges, leading to a more cooperative approach to managing Arctic affairs.
- Escalation of Conflicts: Continued military buildups and competing claims could result in confrontations and conflicts, destabilizing the region and threatening global security.
The Crucial Role of Global Governance
International organizations and treaties will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the Arctic, promoting dialogue, and ensuring sustainable development. Strengthening global governance mechanisms will be essential for fostering cooperation and preventing conflicts in this critical region.
Conclusion: Navigating the Arctic Cold War
In summary, the Arctic Cold War is a multifaceted issue encompassing historical, geopolitical, environmental, and legal dimensions. As nations vie for dominance in this critical region, the potential for conflict grows, underscoring the importance of understanding the dynamics at play. Fostering cooperation and ensuring the peaceful resolution of disputes will be crucial for preserving the Arctic's fragile environment and promoting sustainable development.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights on the Arctic Cold War in the comments below. Your perspectives are valuable as we collectively explore this complex and evolving topic. Thank you for reading, and we encourage you to explore our other articles for further insights and updates on global affairs.